The Data Protection Act (DPA) 2018 is the UK's updated data protection law which became effective on 25th May 2018 and was recently amended on the 1st January 2021 to reflect the United Kingdom's exit from the EU. It sits alongside the UK GDPR and replaces the Data Protection Act 1998. The United Kingdom is […]
What are Cookies and What do They do?
When it comes to websites most people have heard of a cookie but what exactly are they?
Cookies 🍪 are text files held on your computer that store information about you and the website you are visiting. The website sends the cookie to your computer and your computer then stores this information. This information allows the website to remember certain pieces of information when you browse to a different page or start another session.
On this page
What do Cookies do? 🍪

Cookies store information about your activity on a website. For example a cookie will remember your login details so if you close your browser page and reopen it you will still be logged in. They will remember what you have placed in your cart while you are still browsing the site. Without cookies your cart would empty each time you changed pages on a website.
Cookies alone don't pose any threat to your security. They simply store information that has been given to a website. However there are some cookies known as malicious cookies. These cookies track and store your online activity without your knowledge. It is possible that this information can be made available to third party websites.
Types of Cookies
There are a number of different types cookies and each of them have their own functions. The following are some of the more common cookies.
🍪 Session Cookies
Session cookies are temporary cookies that are deleted when your web browser is closed. These cookies require you to log in each time you visit a site as they do not remember your information from one visit to the next.
Examples of session cookies uses are shopping cart, remembering you from one page to the next, and multi media content playing.
🍪 Persistent Cookies
Persistent cookies are cookies which are saved in your browser until you delete them or they they are deleted by your browser when they expire.
Examples of uses of persistent cookies are language selection, authentication, favourites and internal site bookmarks.
🍪 Functionality Cookies
Functionality Cookies allow a website to remember choices that have been made by the you. This then helps create an experience that is tailored just for you.
Examples of uses of functionality cookies are language selection or region selection.
🍪 Performance Cookies
Performance cookies are used to collect information. This information gives feedback on how the website is being used and helps to create a better user experience. Information collected by performance cookies is anonymous.
Examples of uses of performance cookies are tracking the most used pages and error messages.
🍪 Advertisement Tracking Cookies
Advertisement tracking cookies are third party cookies used by advertisers to enable them to to tailor their advertisements to the individual user. Information is collected from your browser about the types of websites you visit. Then advertisements that are most inline with your interests are then presented to you.
🍪 Affiliate Tracking Cookies
Affiliate tracking cookies are stored on your browser when you click on an external link from a website to a new website's product page. This allows the initial website to earn a commission from the product if you make a purchase.
If you use Affiliate cookies or advertisement tracking cookies, you can include relevant clauses using our privacy policy generator.
privacyterms.io team
How Secure are Cookies?
Cookies alone don't pose any threat to your security. They simply store information that has been given to a website. However there are some cookies known as malicious cookies. These cookies track and store your online activity without your knowledge. It is possible that this information can be made available to third party websites.
Managing Cookies in Your Browser
You may wish to delete cookies from your browser at some stage. Please be aware before you delete all cookies that by doing so you will be forgotten when you are returning to sites that normally recognise you and may need to login again.
So, with that said, let's delete some cookies. In this example I will be showing how to manage and delete cookies in Firefox on a Mac.
- Open your browser, this is where your cookies are stored. The most popular browsers are Internet Explorer, Chrome, Firefox, Safari and Edge.
- Locate where the cookies are stored. For example, on my Mac, in Firefox, I choose Firefox in the top left of me screen. This opens a drop down menu.
- From this menu I select preferences and this brings up a new tab. In preferences I scroll down to Cookies and Site Data and here I can choose to clear or manage my data.
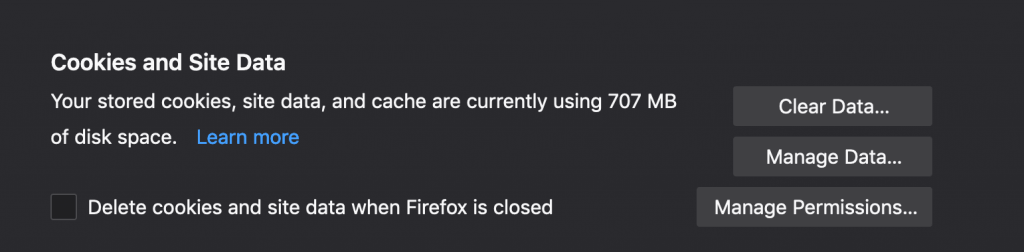
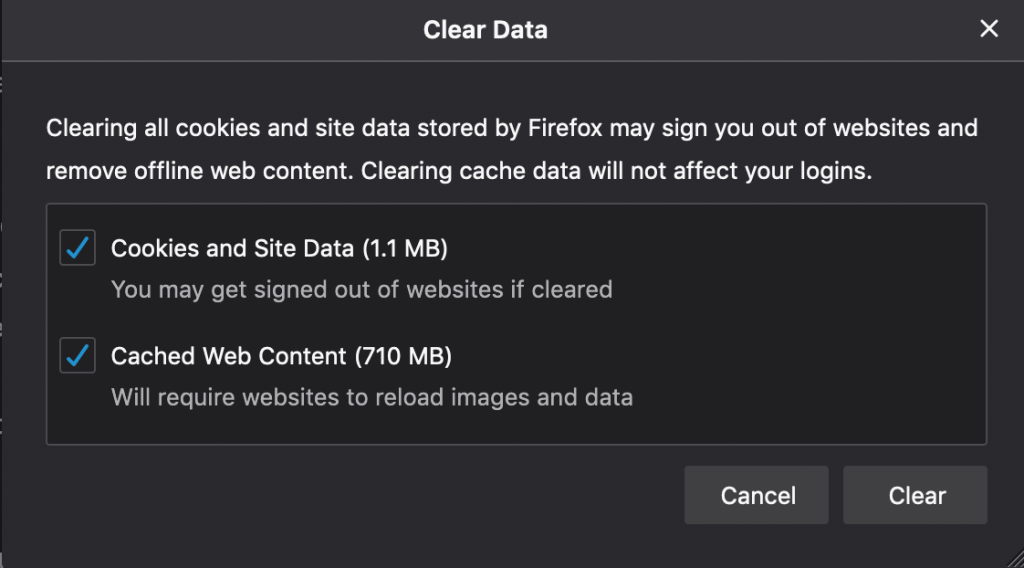
- Clear data. Clearing the data will clear all cookies from all websites you have visited. You will get a warning that clearing all of your cookies may result in you being signed out of websites.
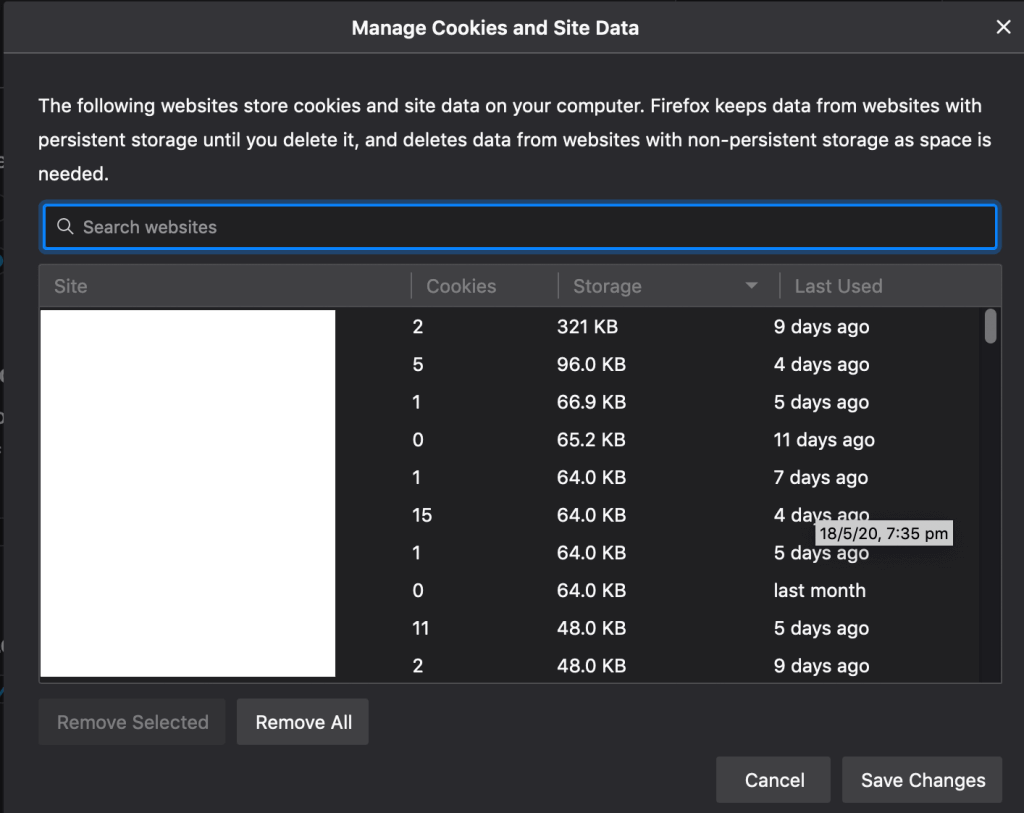
- Manage Data: By selecting to manage your data you will be taken to a screen as shown below. Here you can select which sites you wish to delete cookies from.
- Manage Permissions: here you can select which websites always have permission or never have permission to use cookies and site data.
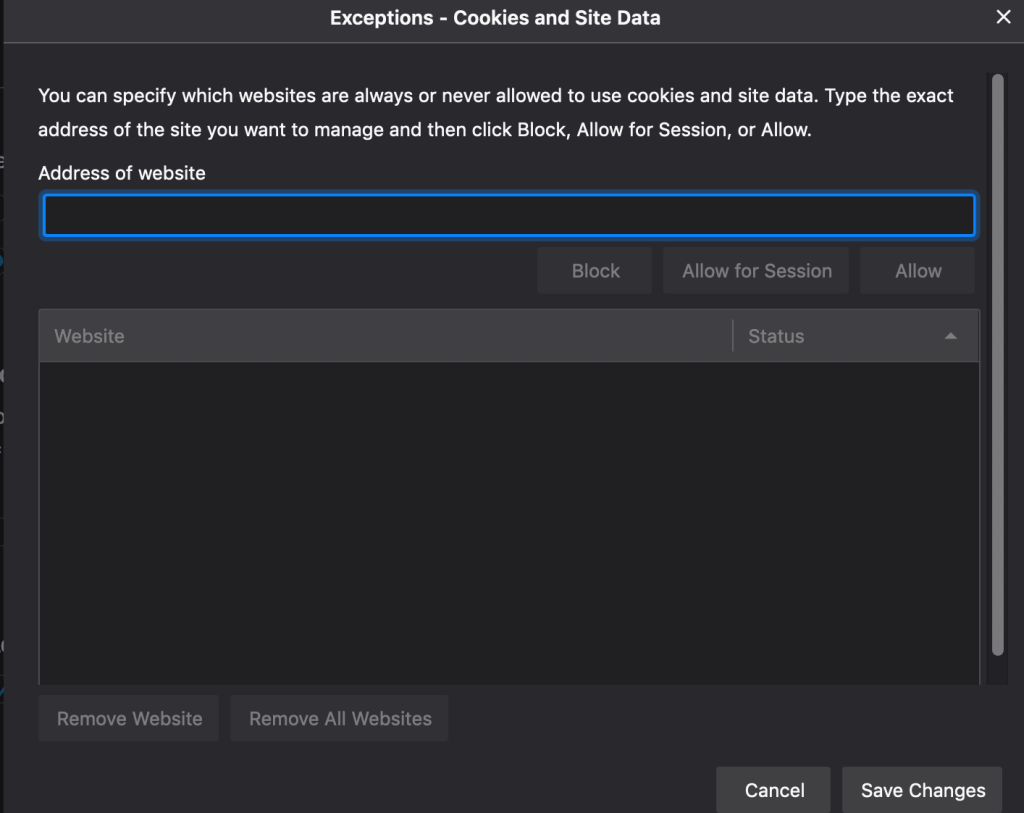
Although I have given an example using Firefox, each browser has an option to manage cookies. In Internet Explorer select Tools then Internet options and lastly the General tab. In Chrome select Menu then Settings and then Show advanced settings. If you cannot find the exact location, Google will be able to help you. Just type in the browser name you are using and delete or manage cookies.
Final Words
In majority of cases cookies are user friendly and harmless. They function to make your online experience seamless and easier. If you are concerned you may have some bad cookies then doing a little clean up will be useful.
Disclaimer
The information in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as legal advice on any matter and does not create a lawyer-client relationship
