The Data Protection Act (DPA) 2018 is the UK's updated data protection law which became effective on 25th May 2018 and was recently amended on the 1st January 2021 to reflect the United Kingdom's exit from the EU. It sits alongside the UK GDPR and replaces the Data Protection Act 1998. The United Kingdom is […]
GDPR Compliance and your Privacy Policy
GDPR compliance refers to your privacy policy's compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (EU) 2016/679. Let's take a look at what it means for the privacy policy of your business.
A Privacy Policy for your website or business is required by law. The purpose of the Privacy Policy is to clearly explain what data is collected, how its collected, used, stored and what the users rights are. So what does this have to do with GDPR?
On this page
General Data Protection Regulation: What is it?
GDPR is an acronym for General Data Protection Regulation. GDPR is a regulation on data, in EU law, that aspires to protect the privacy of the personal data and information relating to each individual citizen of the European Union and the European Economic Area.

The Key Principles of GDPR compliance
There are seven key principles in how data is to be protected in the GDPR, these are:
- Lawfulness, fairness and transparency
- Purpose limitation
- Data minimisation
- Accuracy
- Storage limitation
- Integrity and confidentiality (security)
- Accountability
Let’s take a closer look at these.
Lawfulness, Fairness and Transparency
The personal data of the individual is required to be processed in a lawful, fair and transparent manner.
Purpose Limitation
Personal data is only to be collected for explicit, specific and legitimate purposes. There is to be no further processing of the collected data for any incompatible uses other than its initial use. The following purposes are not deemed incompatible; archiving the data for public interest, scientific or historical research purposes or statistical purposes.
Data Minimisation
Personal data is to be relevant, sufficient and limited to the purpose it is being it is being processed for.
Accuracy
Personal data needs to be as accurate and relevant as possible and any data that is incorrect shall be deleted or rectified without delay.
Storage Limitation
Personal data is to be stored in a way which identifies the data subjects for the least amount of time necessary. Personal data may be held for longer under the following conditions: where it is being used solely for archiving purposes in public interest, for scientific or historical purposes or statistical purposes. In these cases it is necessary that the data be stored in a way that safeguards the individuals’ rights and freedom as set out by the GDPR.
Integrity and Confidentiality (security)
Personal data must be processed in a way which safeguards the security of that personal data. This includes storage that protects against illegal processing, accidental loss, and destruction or damage.
Accountability
Whomever is responsible for the safeguard of the personal data must be able to demonstrate compliance with the previous six points.
These seven principles are the backbone of the GDPR and are good data practice principles. Failure to comply may incur a hefty fine.
The Rights of the Individual
The GDPR sets out the rights of the individual. These rights are:
- The right to be informed
- The right of access
- The right to rectification
- The right to erase
- The right to restrict processing
- The right to data portability
- The right to object
- Rights to automated decision making and profiling.
Let’s take a closer look at these.
1.The right to be Informed
The right to be informed is to provide your user with the information about how you use the personal data you collect from them, how long you retain it and who it will be shared with.
Below is a table listing the privacy information which you should supply to your users
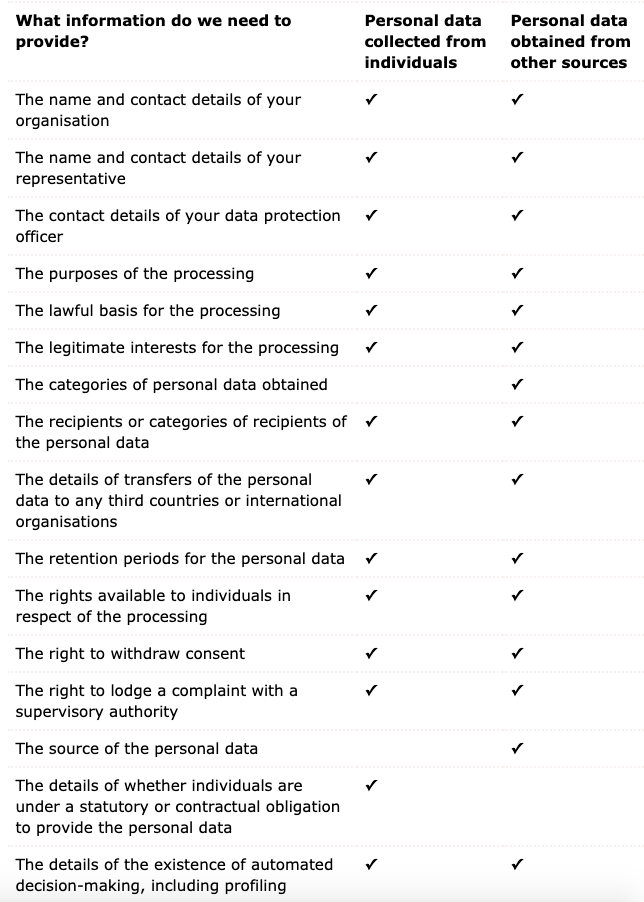
2. The right of access
The right of access may also be known as subject access. It is the right of individuals to access their personal data if they choose. This request must be in written form and in most cases can not be charged for.
3.The right of rectification
The right of rectification means that an individual has the right for incorrect information to be corrected as soon as possible.
4.The right to erasure
The right to erasure may also be referred to as the right to be forgotten. This right means that the individual has the right for their personal data to be erased under certain circumstances.
5.The right to restrict processing
The right to restrict processing refers to the individuals right to have their personal data restricted or suppressed in certain circumstances, therefore limiting the way in which an organisation can use it.
6.The right to data portability
The right to data portability is the right of the individual to obtain, use and move their personal data to another environment for reuse. The data must be transferred in a safe, secure manner.
7.The right to object
The right to object is the right of the individual to object to the processing of their personal data in certain circumstances. They have the right to stop their data being used for the purposes of direct marketing.
8.Rights to automated decision making and profiling.
The rights to automated decision making and profiling states that there must be a lawful basis to use an individuals personal data to carry out profiling or automated decision making. The individual must be given information on how their data is used and they must be linked to the privacy policy if their data has been obtained indirectly.
Detect, Secure, Investigate and Notify
Ensure your policy includes a clause outlining that you are able to detect, protect to the best of your ability, investigate any data breaches and report them to the data subject or supervisory authority within 72 hours.
How Does the GDPR apply to you?
So now you understand the importance of a GDPR compliant privacy policy, how does this affect you?
The GDPR was put in place to protect the rights of the citizens of the EU. However it’s principles apply to any company/organisation/website etc who operate inside or outside of the EU and obtain personal data for any reason from residents within the EU. This is known as the extra-territorial effect.
This is made clear in Article 3 of the GDPR

Benefits of GDPR compliance
The benefits of GDPR compliance and having a GDPR compliant privacy policy are you will receive greater customer confidence and trust. You will also ensure you are in alignment with technological advancements.
Are you GDPR compliant?
Generate your GDPR compliant privacy policy using our privacy policy generator.
Disclaimer
The information in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as legal advice on any matter and does not create a lawyer-client relationship
